Build and Publish Docker image using Jenkins
Today we’re going to learn how to build a Docker image using Jenkinsfile from a git repository and push it to the Docker Hub.
Create a new Jenkins Docker image
The official Jenkins image does not have docker installed in it. So if you try to access docker while running a container based on the official Jenkins image it would result in an error.
How to solve this? we can create a new Jenkins Docker image by preinstalling Docker in it. Following is the Dockerfile that we use to create the new Jenkins Docker image.
FROM jenkins/jenkins:latest
USER root
RUN apt-get update -qq \
&& apt-get install -qqy apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gnupg2 software-properties-common
RUN curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/debian/gpg | apt-key add -
RUN add-apt-repository \
"deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/debian \
$(lsb_release -cs) \
stable"
RUN apt-get update -qq \
&& apt-get install docker-ce=17.12.1~ce-0~debian -y
RUN usermod -aG docker jenkins
Here we use the base image as Jenkins official image, download and install Docker on top of it. Later we use usermod command to change attributes of the docker and jenkins group.
Next, create a docker-compose.yml file to ease the process of Docker image creation.
version: '3'
services:
jenkins:
container_name: 'jenkins-container'
privileged: true
build: .
ports:
- '8080:8080'
- '50000:50000'
volumes:
- myjenkins:/var/jenkins_home
- /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
myjenkins:
Here, we mount a Docker volume myjenkins to /var/jenkins_home directory which lies inside the Docker container and we also map the Docker socket from host to the container.
Build and run the Docker image by executing the following command in the project directory.
docker-compose up
Set up Jenkins
Once Jenkins files have been extracted, the Jenkins server will be fully up and running at http://localhost:8080.
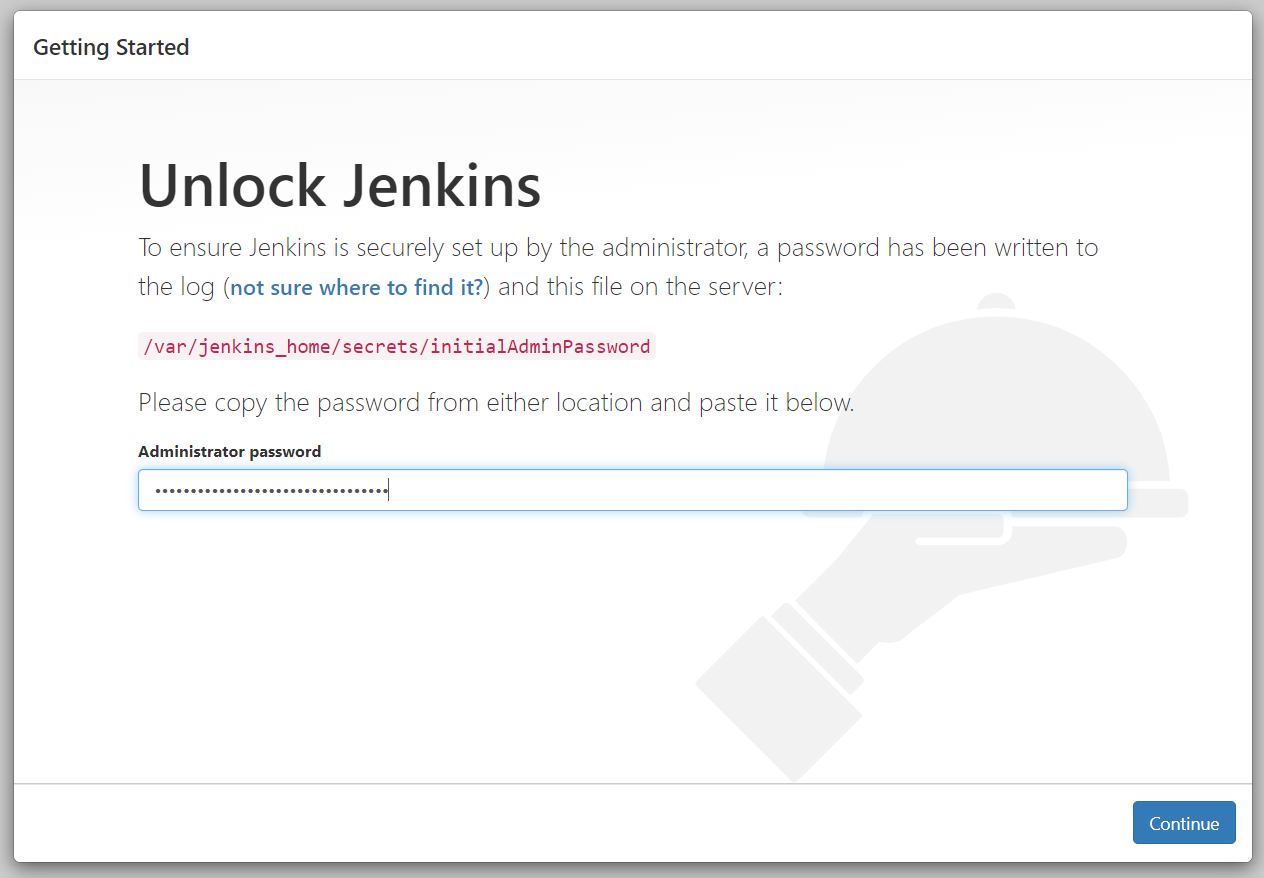
You can find the initial admin password at /var/jenkins_home/secrets/initialAdminPassword as mentioned on the login page.
Next, we can install plugins as per our requirement.
It may take some time depending upon the number of plugins you choose to install. Once the plugins are installed, you will be prompted to create a first admin user which you can skip if you wish to continue as an admin user.
Create Jenkins job
On completion of the initial setup, create a new pipeline in Jenkins by selecting New Item.
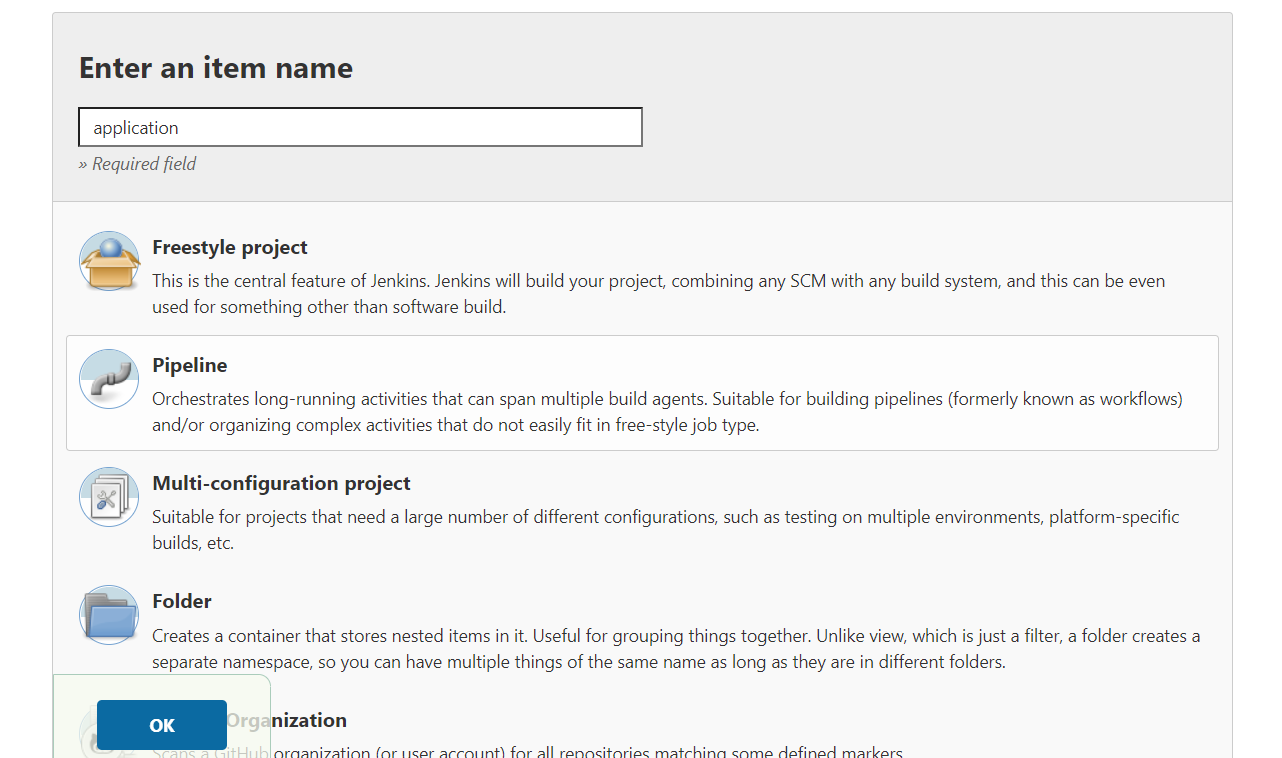
Enter the name of the job and select the type of job you wish to run on Jenkins. We select the Pipeline option since we wish to create a Jenkins pipeline to execute a series of steps.
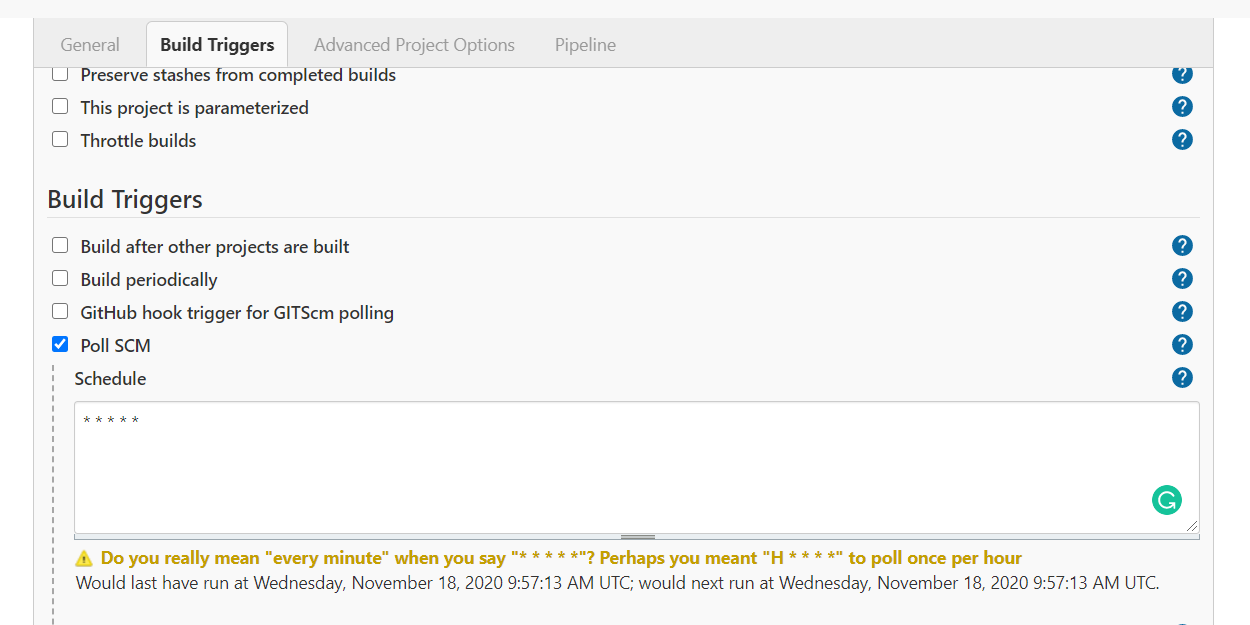
There are multiple options as triggers for Jenkins, however, we use the Polling method and set a schedule as * * * * * which will poll the SCM repository every minute.
Now in the Pipeline section, select the Pipeline script from SCM option, select SCM, and insert the URL of the SCM repository.
You can add credentials for authentication however, credentials are not required for repositories with public access.
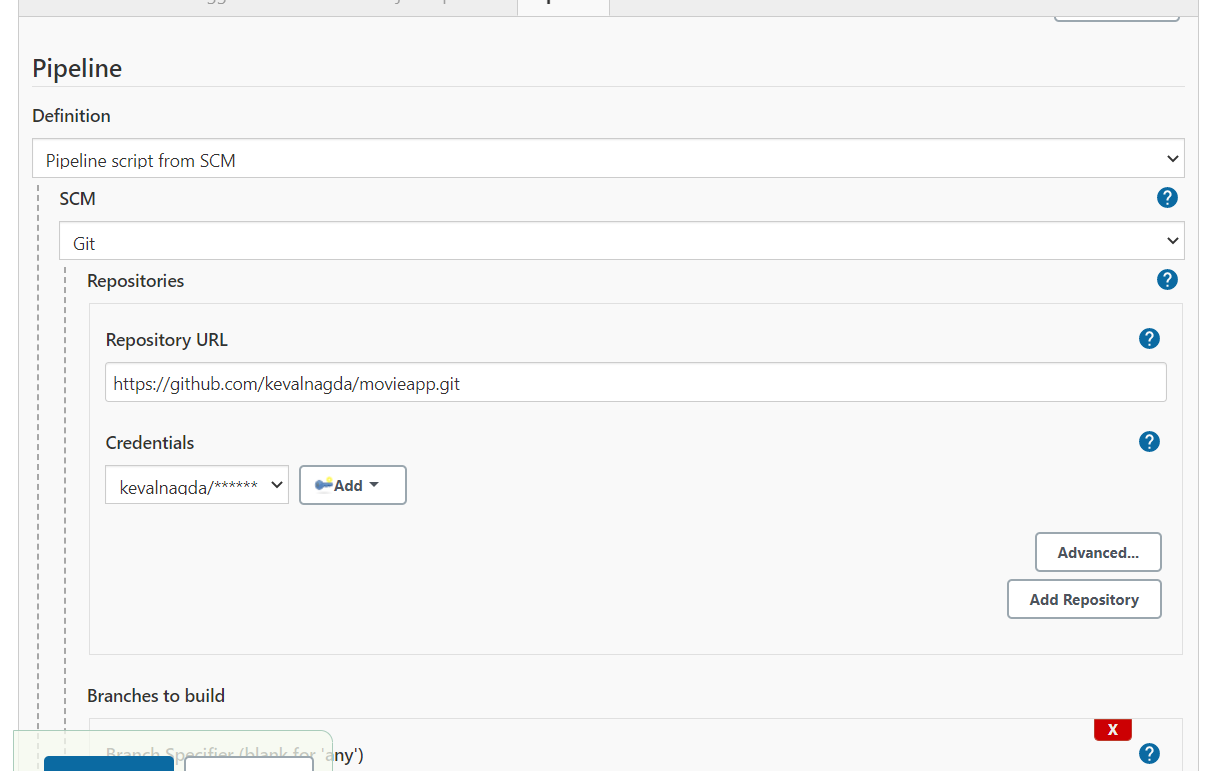
You can also select a specific branch that you wish to build by adding the branch name in the Branch to build section. For example, add */main to build the main branch.
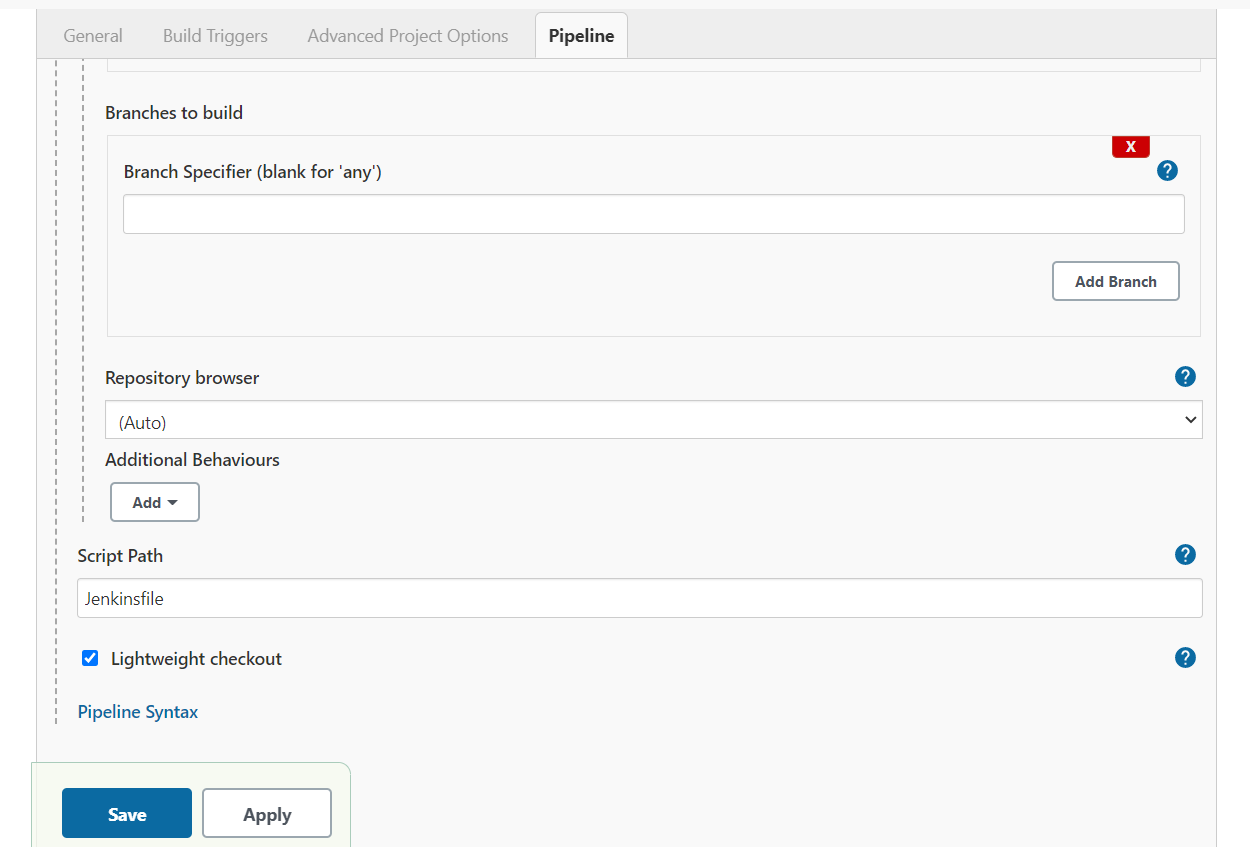
Click the Save button and go to Plugin Manager to install the Docker Build and Publish and Docker Pipeline plugin which helps us to build and push the Docker image to Docker Hub.
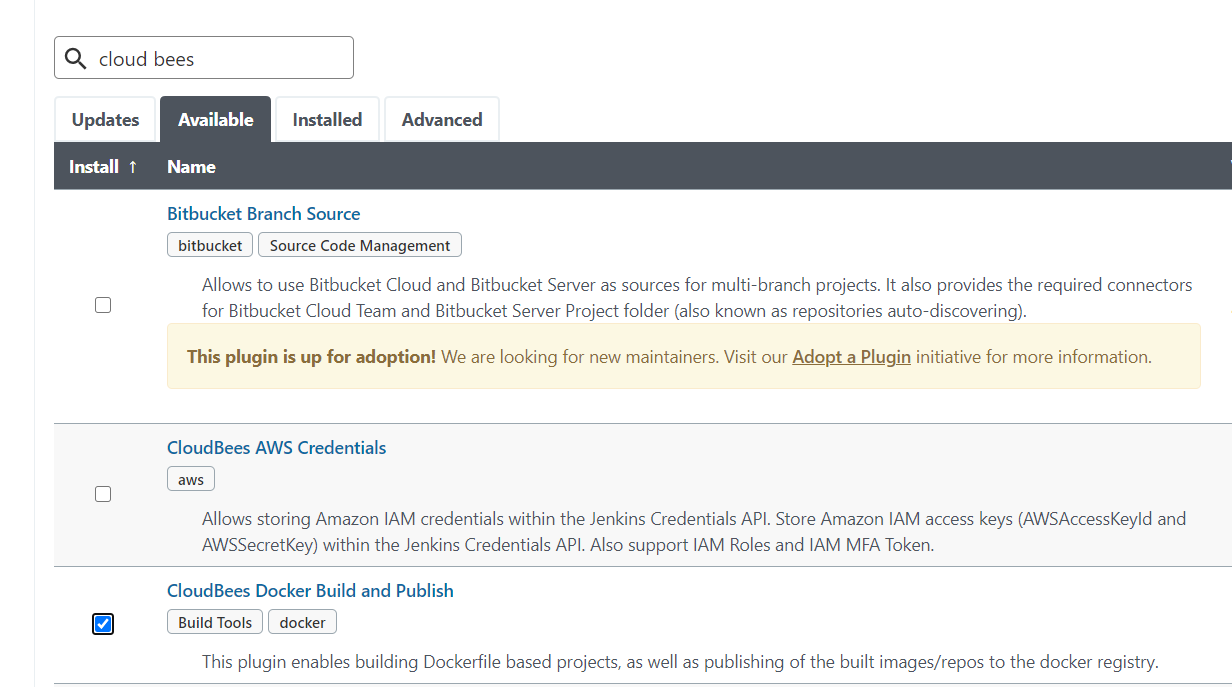
Add Jenkinsfile
Once the plugin has been installed, go ahead and add a Jenkinsfile script given below to the SCM repository which will be used by Jenkins while building a job.
pipeline {
environment {
imagename = "kevalnagda/flaskapp"
registryCredential = 'kevalnagda'
dockerImage = ''
}
agent any
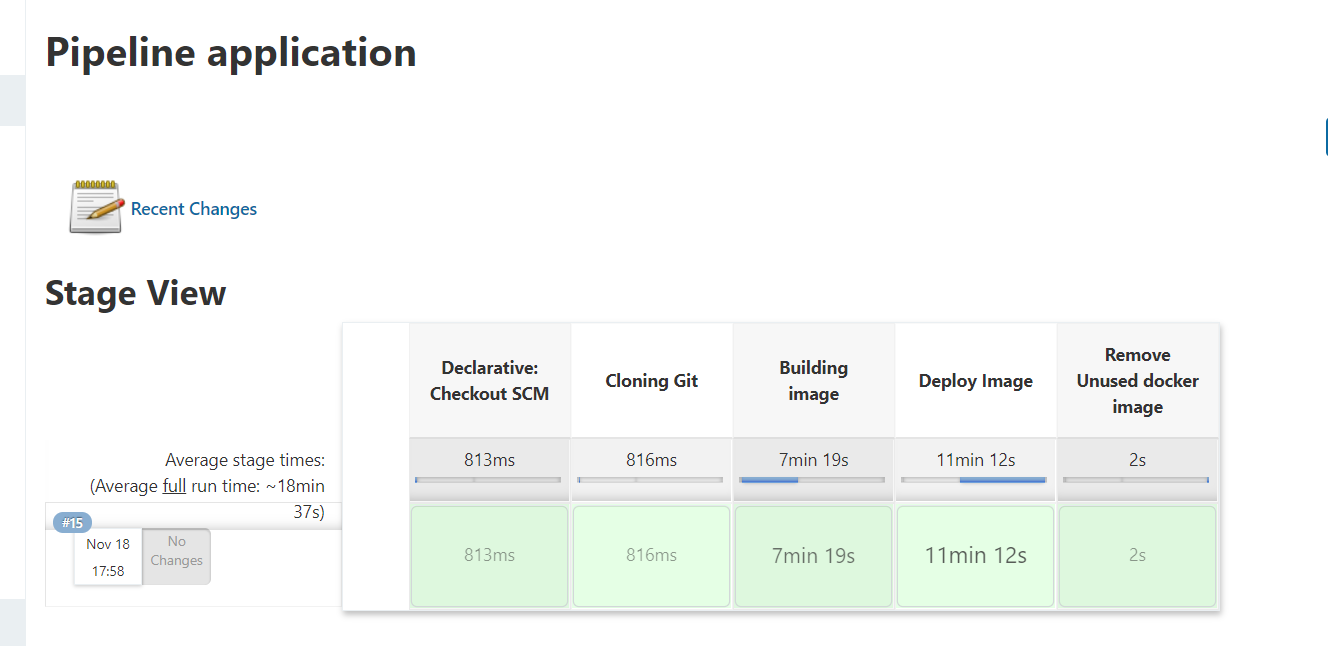
stages {
stage('Cloning Git') {
steps {
git([url: 'https://github.com/kevalnagda/movieapp.git', branch: 'main', credentialsId: 'kevalnagda'])
}
}
stage('Building image') {
steps{
script {
dockerImage = docker.build imagename
}
}
}
stage('Deploy Image') {
steps{
script {
docker.withRegistry( '', registryCredential ) {
dockerImage.push("$BUILD_NUMBER")
dockerImage.push('latest')
}
}
}
}
stage('Remove Unused docker image') {
steps{
sh "docker rmi $imagename:$BUILD_NUMBER"
sh "docker rmi $imagename:latest"
}
}
}
}
Testing
Now, commit changes to the SCM repository to test and see if Jenkins can access the SCM repository and Jenkinsfile.
On successful completion of the job, you would be able to see the latest Docker image in your Docker Hub repository.